Kraft Paper Market Insights: Domestic Prices, Input Cost Analysis, and Emerging Trends by Mr. Pankaj Mishra

Kraft Paper Market Insights: Domestic Prices, Input Cost Analysis, and Emerging Trends by Mr. Pankaj Mishra
-After the failure of opportunistic strategies, the industry is now experiencing a return to more stable, normal pricing
The article below is written by Mr. Pankaj Mishra, Head of Sales & Marketing of Vamshadhara Paper Mills Ltd (Sennars), specialises in kraft paper (both lower and higher gsm) and newsprint paper for diverse applications like packaging, printing, and publishing.
The Pulp and Paper Times
Market Overview.
The Indian Kraft Paper Market has been facing challenges in FY 2024. The primary issues include an oversupply due to high production capacity and low consumption. Additionally, the availability of domestic raw materials has been inconsistent, and the fluctuating prices of Kraft paper have added to the difficulties. As a result, nearly all paper mills are struggling to sustain operations.
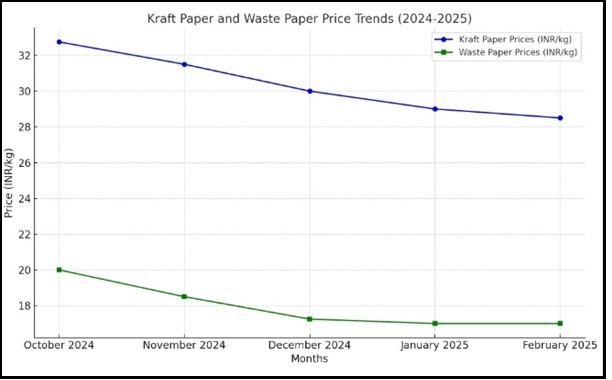
Domestic Price and Waste Paper Scenario.
The fluctuations in Kraft Paper prices over the past months seem to reflect the interplay of raw material costs, supply-demand dynamics, and broader market conditions.
• October 2024: Kraft Paper prices reached INR 32.50-33.00 per kg (Ex-mill), primarily due to elevated costs of domestic and imported waste paper.
• November 2024 Onward: Prices began a downward trend, influenced by softening raw material prices, weekend demand and shifting market dynamics.
• Waste Paper Costs: Local waste paper prices fell from INR 19-21 per kg (September-October 2024) to INR 17.00-17.50 per kg in the South Zone. However, challenges in availability suggest supply chain issues or reduced collection efficiency, which might counteract further price declines.
This scenario highlights the volatility in the paper industry, where raw material availability and pricing play a crucial role. If scrap paper supply remains constrained over the next 3-4 months, it could stabilize or potentially reverse the current downward trend in kraft paper prices.
Export Scenario:
1.Export volumes have declined significantly.
2.Export prices are currently far below the manufacturing costs that Indian mills can sustain.
3.Excess supply and weak demand are driving prices down, creating a critical situation for paper mills. If this trend continues, many mills may face closures in the long term.
4.Elevated ocean freight costs are making exports economically unviable.
5.Increased competition from newly established international mills is compelling buyers to reduce their orders from India.
Paper Import growth in various segments: reason and future anticipation
The Indian paper industry has seen a significant rise in imports, particularly in the uncoated writing and printing segment and specialty grades. As major economies like the US and Europe face economic downturns, international mills are increasingly turning to markets like India. Trade dynamics and agreements with countries such as Indonesia, South Korea, and Thailand are making imports more attractive, with competitive pricing being a key driver for the increased inflow of goods.
To compete with international mills, Indian manufacturers must focus on three key factors: quality, affordability, and sustainability. While customers continue to prioritize quality, they also seek a better experience at a reasonable price, especially amid ongoing inflationary pressures.
Input Cost analysis and pulp price scenario
Although there is a lack of specific and comprehensive data on pulp prices in India, it is crucial to monitor global trends as they often influence domestic markets. India’s paper industry is heavily reliant on imported pulp, and fluctuations in global pulp prices can directly impact the cost structure for domestic paper manufacturers. Currency fluctuations and global shipping costs also play a significant role in determining the final cost of imported pulp in India.
Potential Impact on Domestic Paper Production: If global pulp prices continue to rise, Indian manufacturers may face higher production costs, which could lead to higher paper prices in the domestic market. On the other hand, if pulp prices stabilize or decrease, manufacturers could see some relief. It is essential for Indian producers to keep track of these trends to anticipate changes in input costs and adjust their pricing strategies accordingly.
Weak Global Paper Demand: Reduced paper demand globally is a significant factor. This could be driven by shifts toward digital alternatives, changing consumer behavior, or economic downturns. Lower demand means less need for raw materials like pulp, putting downward pressure on prices.
Mills' Opportunistic Strategies: Initially, paper mills tried to capitalize on short-term price hikes by creating an artificially favorable market. These could have been based on limited supply or strategic inventory management. However, this approach has not been sustainable, likely due to overproduction or external economic factors pushing prices back down.
Return to Normal Pricing: After the failure of opportunistic strategies, the industry is now experiencing a return to more stable, normal pricing. This suggests that the market is adjusting to the realities of supply and demand, which could lead to more predictable pricing in the future but likely at lower levels than the peaks seen during more speculative periods.
Red Sea Crisis impact on domestic paper market | Mill and Traders
The ongoing Red Sea Crisis has significantly disrupted global shipping routes, with serious consequences for the paper industry, particularly in India. This region relies heavily on imported waste paper and other raw materials, making it vulnerable to such geopolitical disturbances. Here’s how this crisis is impacting mills and traders in the domestic paper market:
1. Raw Material Costs: Indian paper mills, especially those producing kraft paper, rely on imported waste paper, mainly from the U.S. and Europe. The Red Sea disruptions have increased shipping costs dramatically—by up to 100%—and caused delays in raw material supplies.
2. Operational Challenges: Mills face reduced availability of high-quality fiber (such as OCC and DS OCC grades) and rising domestic production costs.
3. Market Dynamics: Rising costs have led to price increases for both kraft and finished paper products. Traders are passing these costs to end-users, particularly in the packaging and publishing sectors. However, the increased availability of cheaper imports from ASEAN countries under free trade agreements is creating competitive pressure for domestic mills.
4. Supply Chain Issues: Container shortages and longer transit times due to detours in the Red Sea region have disrupted global trade flows, causing supply inconsistencies. This has particularly affected imports to India, where higher freight rates have made the country less competitive in global trade.
The Red Sea Crisis is straining the domestic paper market by driving up costs, disrupting supply chains, and intensifying competition from imports. The situation demands close monitoring and possible intervention to stabilize the market and ensure supply continuity.
About:
Vamshadhara Paper Mills Ltd., specialises in kraft paper (both lower and higher gsm) and newsprint paper for diverse applications like packaging, printing, and publishing. The company prioritizes sustainability, sourcing raw materials responsibly, minimizing waste, and ensuring no harm to the local community.
With a strong commitment to customer satisfaction, Vamshadhara Paper Mills has grown significantly. Its Srikakulam facility in North coastal Andhra Pradesh produces 4200 TPM of Newsprint and Kraft varieties. The white division boasts a state-of-the-art paper machine using recycled fibers and advanced technologies.
Web Title: Kraft Paper Market Insights: Domestic Prices, Input Cost Analysis, and Emerging Trends by Mr. Pankaj Mishra




 Join WhatsApp Group
Join WhatsApp Group Join Telegram Channel
Join Telegram Channel Join YouTube Channel
Join YouTube Channel Join Job Channel (View | Submit Jobs)
Join Job Channel (View | Submit Jobs) Join Buy Sell Channel (Free to Submit)
Join Buy Sell Channel (Free to Submit) Paper News Headlines Channel (Free to read)
Paper News Headlines Channel (Free to read)















